China is the world’s largest fertilizer producer and consumer, driven by its vast agricultural sector. The market is dominated by nitrogen (urea), phosphate, and potassium fertilizers, with significant government influence through subsidies, production quotas, and environmental regulations. Key players include state-owned enterprises like Sinochem and private firms such as Kingenta.
Recent trends focus on sustainable practices, including controlled-release and organic fertilizers, amid stricter environmental policies. Despite overcapacity challenges, exports remain strong, particularly to Asia and Africa. The market is gradually shifting toward high-efficiency and eco-friendly products to align with China’s “green agriculture” goals. Price volatility, raw material costs, and trade policies are critical factors shaping the industry.
I. Current Industry Landscape
Market Scale & Supply-Demand Structure
-
Production & Demand:
-
2024 output: 81.4 MMT (million metric tons)
-
2024 demand: 82.5 MMT
-
Market value: ¥733.59 billion ($102.3B USD, +2.8% YoY)
-
2025 Projection: Output to exceed 80 MMT with high-value segments accelerating
-
-
Product Mix:
-
Conventional fertilizers dominate (>90% share)
-
Organic/microbial fertilizers growing at 18% CAGR (current share <10%)
*Supplement: Global bio-stimulant market to hit $6.2B by 2027 (Research and Markets)*
-
Policy-Driven Green Transition
-
Efficiency Mandates:
-
43% fertilizer utilization rate target by 2025 (vs. 38% in 2020)
-
15% organic substitution ratio for conventional NPK
-
-
Carbon Compliance:
-
EU CBAM adds 23% cost to urea exports (emitting 1.5-2 tCO₂/t)
-
Green ammonia tech adoption reduces carbon footprint by 52%
Supplement: Yara’s electrified ammonia pilot cuts emissions by 90% (IFA Case Study)
-
Trade Volatility
| Indicator | 2024 H1 Performance | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| Exports | 12.6 MMT (-24.9% YoY) | Red Sea shipping disruptions |
| Imports | 7.2 MMT | Geopolitical supply risks |
| Major Imports | MOP, NPK compounds | Israel-Egypt gas conflict impact |
II. Competitive Structure: Fragmentation vs Consolidation
Key Players
-
Market Leaders:
-
Yuntianhua: 5.55 MMT phosphate capacity
-
Yanhu Group: Potash dominance (Qinghai reserves)
-
Xinyangfeng: Compound fertilizer innovation
-
CR10 concentration: >60% (vs. 45% in 2020)
-
-
Niche Specialists:
-
Genliduo: Microbial fertilizers
-
Muyuan Foods: Manure-to-organic fertilizer recycling
-
Regional Capacity Allocation
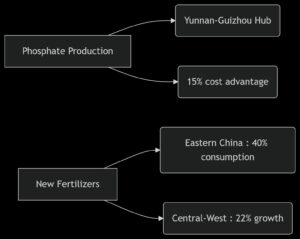
III. Emerging Trends & Growth Vectors
Green Technology Leap
-
Smart Manufacturing:
-
AI-optimized microbial strains (e.g., *GS-89 nitrogen-fixer*) reduce R&D cycles by 30%
-
IoT-enabled fermentation monitoring cuts defects by 25%
-
-
Nano-Coating Breakthroughs:
-
Organic fertilizer release efficiency ↑ to 60%
-
Market impact: Controlled-release fertilizers to reach ¥150B ($21B) by 2030
-
Global Expansion Strategy
-
Target Markets:
-
Southeast Asia: Vietnam/Indonesia compound plant investments
-
Africa: 30 MMT demand gap (40% self-sufficiency)
-
-
Trade Barrier Mitigation:
-
CBAM cost absorption via green certification
-
Potassium supply diversification (Canada/Belarus alternatives)
-
Policy-Demand Synergy
-
Domestic Initiatives:
-
Black soil conservation → Drought-resistant humic acid fertilizers
-
Saline-alkali land remediation → Seaweed-acid compound demand
-
-
International Shifts:
-
India’s nano-urea adoption → 10% conventional urea demand destruction
-
EU organic-inorganic blend growth: 12% CAGR
-
IV. Investment Framework & Risk Management
Strategic Focus Areas
| Sector | Opportunity | Target Players |
|---|---|---|
| Tech Leaders | Bio-fermentation/IP-controlled release | Microbial strain developers |
| Resource Integrators | Manure/straw recycling systems | Muyuan Foods model |
| Global First-Movers | ASEAN/Africa distribution hubs | Yuntianhua overseas JVs |
Risk Mitigation Toolkit
-
Technology Risks:
-
University-industry R&D partnerships (e.g., China Agricultural University菌种labs)
-
Automated fermentation systems ↓ process variability
-
-
Market Adoption Barriers:
-
Demonstration farms + rural e-commerce penetration
-
-
Policy Dependency:
-
Functional organic fertilizers (high regulatory barriers)
-
Conclusion: Triple Transformation Imperative
China’s 2025 fertilizer evolution hinges on:
-
Premiumization of conventional products (energy-efficient urea)
-
Biological Acceleration (18% CAGR for bio-stimulants)
-
Globalization 2.0 (Africa/ASEAN export infrastructure)
Critical Success Factors:
-
Carbon-neutral certification for EU market access
-
Modular organic production for rural revitalization
-
Geopolitical hedging via potash equity investments







