The European Union’s fertilizer market, encompassing 179.9 million hectares of agricultural land (27 billion mu) with 133.9 million hectares under fertilization, operates under a sophisticated regulatory framework. This article examines the intersecting requirements of REACH (EC 1907/2006), Fertilizing Products Regulation (FPR EU 2019/1009), CE marking, and biostimulant registration that govern the €32.9 billion fertilizer sector. With nitrogen fertilizers constituting 47% of EU imports and biostimulants growing at 10.43% CAGR, compliance is essential for market access.
Import Dependency
| Fertilizer Type | Import Share of consumption | Key Suppliers |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen Fertilizers | 32% | 47% Nitrates (dominant) |
| Phosphate | 65% | 50% from Morocco OCP Group |
| Raw Materials | 88% | 30% from Russia and Belarus |
| Biostimulants | €2.9B market | 10.43% CAGR |
GAGR=Compound Annual Growth Rate
2. Regulatory Framework Architecture
Regulatory Requirements for Fertilizer Products Entering the EU Market
-
Fertilizer Raw Materials: Substances or mixtures used in fertilizer production, primarily regulated under REACH.
-
Finished Fertilizer Products: Products ready for sale to end-users in agriculture, which must comply with both FPR and REACH regulations.
-
CE Marking: The core prerequisite for finished fertilizers is compliance with the EU Fertilizing Products Regulation (FPR).
2.1 REACH Regulation (EC 1907/2006)
Core Obligations:
-
Registration: Mandatory for substances >1 ton/year (dossier to ECHA)
-
Evaluation: Risk assessment by Member States
-
Authorization: Required for SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern)
-
Restriction: Bans on hazardous substances
Compliance Entities:
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Non-EU Manufacturers | Appoint Only Representative (OR) |
| EU Importers | Full REACH compliance |
| Downstream Users | Implement exposure controls |
2.2 Fertilizing Products Regulation (FPR EU 2019/1009)
Product Functional Categories (PFCs):
| PFC | Scope | REACH Trigger |
|---|---|---|
| PFC 1: Fertilizers | Inorganic/Organic NPK | CMC 1,3,4,5,6 |
| PFC 3: Soil Improvers | Biochar, Gypsum | Case-specific |
| PFC 6: Biostimulants | Microbial/Non-microbial | Mandatory |
Component Material Categories (CMCs):
-
High-Risk CMCs (1,3,4,5,6): REACH registration mandatory for CE marking
-
Other CMCs (2,7,8,9,10): REACH required if >1 ton/year imported
3. CE Marking Implementation Pathway
Conformity Assessment Modules
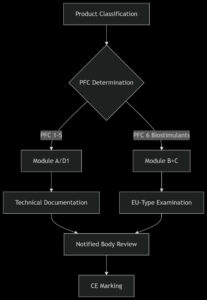
Documentation Requirements:
-
Chemical Safety Report (REACH Annex I)
-
Efficacy Data (CEN/TS 17700-1 for biostimulants)
-
Contaminant Testing:
-
Heavy metals (Cd <60mg/kg P₂O₅)
-
Pathogens (Salmonella spp. absent in 25g)
-
-
Declaration of Conformity (DoC)
4. Biostimulant Compliance (PFC 6)
4.1 Technical Requirements
| Parameter | Microbial | Non-microbial |
|---|---|---|
| Viability | >10⁹ CFU/g | N/A |
| Heavy Metals | As<40mg/kg | As<30mg/kg |
| Efficacy Proof | 2-season trials | 3-location studies |
| Label Claims | Strain ID + CFU | Active substance % |
4.2 Certification Process
-
Module B: Product design verification (Notified Body)
-
Module C: Manufacturing audit (ISO 9001 alignment)
-
Surveillance: Annual batch testing
5. Strategic Compliance Roadmap
5.1 REACH Registration Workflow

5.2 Cost Optimization Strategies
-
Consortium Registration: Share data costs for same substances
-
CMC Optimization: Select CMC 7/8/9 to avoid REACH (<1 ton)
-
Local Formulation: Blend imported raw materials in EU to avoid importer status
6. Penalty Framework for Non-Compliance
| Violation | Penalty Range | Regulatory Basis |
|---|---|---|
| Unregistered SVHC | €500,000-5M | REACH Art. 41 |
| Exceeding contaminant limits | Product recall + 15% annual turnover | FPR Art. 12 |
| False biostimulant claims | Market ban + €2M fine | EU 2026/1432 |
7. Future Regulatory Developments (2025-2027)
-
Digital Product Passports: QR codes linking to REACH/FPR dossiers (2026 mandate)
-
Carbon Footprint Declarations: Required for nitrogen fertilizers (ISO 14067)
-
Microplastic Restrictions: Polymer-coated fertilizers under REACH Annex XVII
“The REACH-FPR nexus represents the world’s most stringent fertilizer regulatory regime. Non-EU producers must integrate compliance into R&D phases to avoid 24-month market delays.”
— European Chemicals Agency (ECHA)







